
by Robyn Bolton | Nov 6, 2024 | Leadership, Tips, Tricks, & Tools
Corporate offsites – the phrase conjures images of everything from “mandatory fun” with colleagues to long and exhausting days debating strategy with peers. Rarely are the images something that entice people to sit up and shout, “YEA!” But what if the reality could be something YEA! worthy?
That’s exactly what the authors of the recent HBR article, “Why Offsites Work – and How to Get the Most Out of Them,” describe and offer a guide to accomplish.
Offsites May Be the Answer to the WFH vs. RTO Debate
Offsites aren’t new but they’ve taken on a new role and new significance as companies grapple with how to manage Work from Home (WFH) and Return To Office (RTO) policies.
As with most things in life, the pendulum swings from one extreme to another until eventually, finally, landing in a stable and neutral midpoint. When the pandemic hit, we swung from every day in the office to every day at home. Then society opened back up and corporate landlords came calling for rent, whether or not people were in the offices, so we swung back to Return to Office mandates.
Offsites, the authors suggest, may be the happy medium between the two extremes because offsites:
“give people opportunities for interactions that otherwise might not happen. Offsites create unique opportunities for employees to connect in person, forming new relationships and strengthening existing ones. As a result, offsites help people learn about others’ knowledge and build interpersonal trust, which are both critical ingredients for effective collaboration.”
Offsite Connections Lead to Collaborations that Generate ROI
After analyzing eight years of data from a global firm’s offsites and 350,000 “instances of formal working relationships” for 750 employees, the authors found that intentionally designed offsites (more on that in a moment) yield surprisingly measurable and lasting results:
- 24% more incoming requests for collaboration amongst attendees post vs. pre-offsite (silos busted!)
- 17% of new connections were still active two years after the offsite (lasting change!)
- $180,000 in net new revenue from collaborations within the first two months post offsite (real results!)
The benefits event extended to non-attendees because they “seemed to get the message that collaboration is important and wanted to demonstrate their commitment to being collaborative team players” and “likely identified new collaborators after the offsite through referrals.”
How to Design Offsites That Get Results
Four key strategies emerged from the authors’ research and work with over 100 other organizations:
- Design for the people in the audience, not the people on stage. Poll attendees to understand their specific needs and goals, then design collaborative activities, not management monologues.
- Design for the new hires, not the tenured execs. Create opportunities for new hires to meet, connect with, and work alongside more experienced colleagues.
- Set and communicate clear goals and expectations. Once the offsite is designed and before it happens, tell people what to expect (the agenda) and why to expect it (your design intentions and goals). Also, tell them how to make the most of the offsite opportunities by thinking about the skill and network gaps they want to fill.
- Track activities to measure ROI. The connections, collaborations, and commitments that start at the offsite need to continue after it in the form of ongoing communication, greater collaboration, and talent engagement. Yes, conduct a post-event survey immediately after the event but keep measuring every 2-3 months until the next offsite. The data will reveal how well you performed against your goals and how to do even better the next time.
Offsites can be a powerful tool to build an organization’s culture and revenue, but only if they are thoughtfully designed to go beyond swanky settings, sermons from the stage, and dust-collecting swag and build the connections and collaborations that only start when people are together, in-person, outside of the office.

by Robyn Bolton | Oct 22, 2024 | Leadership, Tips, Tricks, & Tools
How many times a day do you ask someone to do something? If you total all the requests you make of coworkers, family members, friends, people at restaurants and shops, and even strangers, the total is somewhere between 100 and 1 bazillion. Now, what if I told you that by including just one word in your request, the odds of receiving a positive response increase by 50%?
And no, that word is not “please.”
The real magic word
Harvard 1978. Decades before everyone had access to computer labs, home computers, and personal printers, students had to line up at the copy machine to make copies. You could easily spend hours in line, even if you only had a few copies to make. It was an inefficient and infuriating problem for students.
It was also a perfect research opportunity for Ellen Langer, a professor in Harvard’s Psychology Department.
Prof. Langer and her colleagues asked students to break into the line using one of three phrases:
- “Excuse me, I have 5 pages. May I use the xerox machine?”
- “Excuse me, I have 5 pages. May I use the xerox machine, because I have to make copies?”
- “Excuse me, I have 5 pages. May I use the xerox machine, because I’m in a rush?”
The results were definitive and surprising. Students who used the first phrase were successful 60% of the time, but those who used the phrases with “because” were successful 93% and 94% of the time.
“Because” matters. The reason does not.
Note that in phrases 2 and 3, the reason the student is asking to cut in line isn’t very good. You can practically hear the snarky responses, “Of course, you have to make copies; why else would you be at the copy machine?” or “We’re all in a rush,” and the request is denied.
But that didn’t happen.
Instead, the research (and hundreds of subsequent studies) showed that when the ask is simple or familiar, people tend to follow instructions or respond positively to requests without paying attention to what’s said, even if the instructions don’t make sense or the request disadvantages them in some way. Essentially, people hear “because,” assume it’s followed by a good reason and comply.
“Because” matters. How you use it matters more.
The power of “because” isn’t about manipulation or coercion. It’s about fostering a culture of transparency, critical thinking, and effective communication.
Taking the time to think about when and how to communicate the Why behind your requests increases your odds of success and establishes you as a strategic and thoughtful leader. But building your “Because’ habit takes time, so consider starting here:
Conduct a “Because” Audit: For one day, track your use of “because.” How many times do you make a request? How many times to you explain your requests with “because?” How many times do you receive a request, and how many of those include “because?” Simply noticing when “because” is used and whether it works provides incredible insights into the impact it can have in your work.
Connect your “Becauses” As leaders, we often focus on the “what” and “how” of directives, but the “why” is equally crucial. Take your top three strategic priorities for the quarter and craft a compelling “because” statement that clearly articulates the reasoning behind it. For instance, “We’re expanding into the Asian market because it represents a $50 billion opportunity that aligns perfectly with our core competencies.” This approach not only provides clarity but also helps in rallying your team around a common purpose.
Cascade the “Because” Habit: Great leaders don’t just adopt best practices; they institutionalize them. Challenge your direct reports to incorporate “because” into their communications. When they bring you requests, ask them for the “because’ if they don’t offer it. Make it a friendly competition and celebrate people who use this technique to drive better outcomes.
Tell me how you’ll start because then you’re more likely to succeed.
(see what I did there?)

by Robyn Bolton | Oct 14, 2024 | Innovation, Leadership, Stories & Examples
Once upon a time, in a lush forest, there lived a colony of industrious beavers known far and wide for their magnificent dams, which provided shelter and sustenance for many.
One day, the wise old owl who governed the forest decreed that all dams must be rebuilt to withstand the increasingly fierce storms that plagued their land. She gave the beavers two seasons to complete it, or they would lose half their territory to the otters.
The Grand Design: Blueprints and Blind Spots
The beaver chief, a kind fellow named Oakchew, called the colony together, inviting both the elder beavers, known for their experience and sage advice and the young beavers who would do the actual building.
Months passed as the elders debated how to build the new dams. They argued about mud quantities, branch angles, and even which mix of grass and leaves would provide structural benefit and aesthetic beauty. The young beavers sat silently, too intimidated by their elders’ status to speak up.
Work Begins: Dams and Discord
As autumn leaves began to fall, Oakchew realized they had yet to start building. Panicked, he ordered work to commence immediately.
The young beavers set to work but found the new method confusing and impractical. As time passed, progress slowed, panic set in, arguments broke out, and the once-harmonious colony fractured.
One group insisted on precisely following the new process even as it became obvious that they would not meet the deadline. Another reverted to their old ways, believing that a substandard something was better than nothing. And one small group went rogue, retreating to the smallest stream to figure it out for themselves.
As the deadline grew closer, the beavers worked day and night, but progress was slow and flawed. In desperation, Oakchew called upon the squirrels to help, promising half the colony’s winter food stores.
Just as the first storm clouds gathered, Oakchew surveyed the completed dams. Many were built as instructed, but the rushed work was evident and showed signs of weakness. Most dams were built with the strength and craftsmanship of old but were likely to fail as the storms’ intensity increased. One stood alone and firm, roughly constructed with a mix of old and new methods.
Wisdom from the Waters: Experiments and Openness
Oakchew’s heart sank as he realized the true cost of their efforts. The beavers had met their deadline but at a great cost. Many were exhausted and resentful, some had left the colony altogether, and their once-proud craftsmanship was now shoddy and unreliable.
He called a final meeting to reflect on what had happened. Before the elders could speak, Oakchew asked the young beavers for their thoughts. The colony listened in silent awe as the young builders explained the flaws in the “perfect” process. The rogue group explained that they had started building immediately, learning from each failure, and continuously improving their design.
“We wasted so much time trying to plan the perfect dam,” Oakchew admitted to the colony. “If we had started building sooner and learned from our mistakes, we would not have paid such a high cost for success. We would not have suffered and lost so much if we had worked to ensure every beaver was heard, not just invited.”
From that day forward, the beaver colony adopted a new approach of experimentation, prototyping, and creating space for all voices to be heard and valued. While it took many more seasons of working together to improve their dams, replenish their food stores, and rebuild their common bonds, the colony eventually flourished once more.
The Moral of the Story (just in case it isn’t obvious)
The path to success is paved not with perfect plans but with the courage to act, the wisdom to learn from failures, and the openness to embrace diverse ideas. True innovation arises when we combine the best of tradition with the boldness of experimentation.
by Robyn Bolton | Oct 9, 2024 | Innovation, Leadership
In our race to enable and support hybrid teams, our reliance on collaboration software has inadvertently caused us to forget the art of true collaboration.
The pandemic forced us to rely on digital platforms for communication and creativity. But as we embraced these tools, something essential was lost in translation. Last week, I watched team members sitting elbow-to-elbow spend two hours synthesizing discovery interviews and debating opportunity areas entirely by chat.
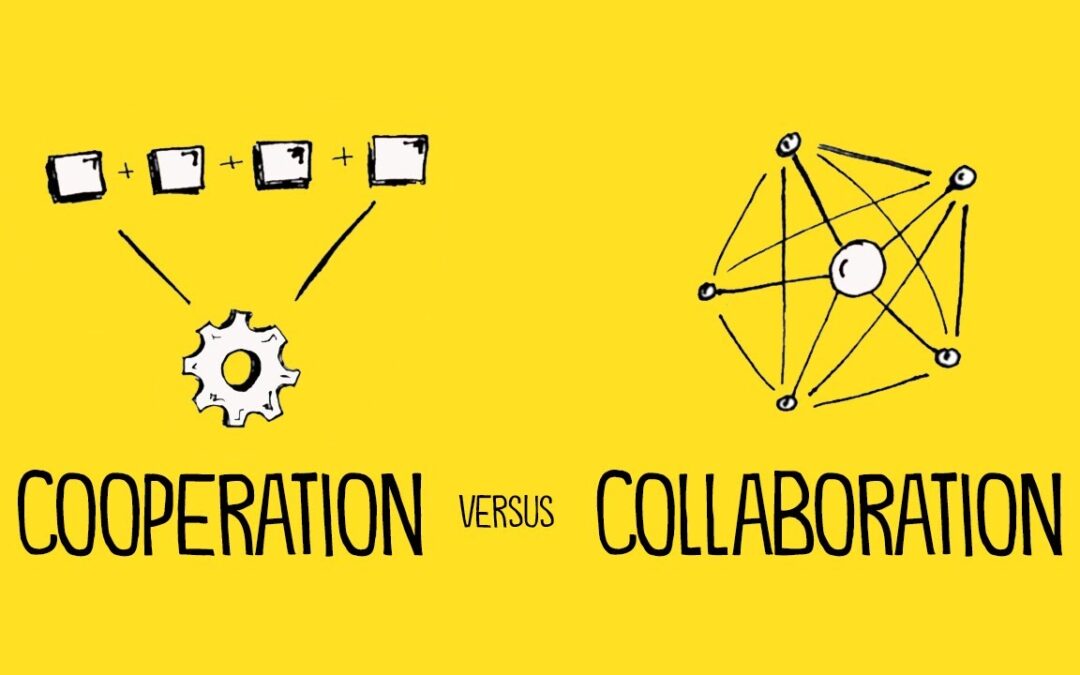
What collaboration is
“Collaboration” seems to have joined the ranks of meaningless corporate buzzwords. In an analysis of 1001 values from 172 businesses, “collaboration” was the #2 most common value (integrity was #1), appearing in 23% of the companies’ value statements.
What it means in those companies’ statements is anyone’s guess (we’ve all been in situations where stated values and lived values are two different things). But according to the dictionary, collaboration is “the situation of two or more people working together to create or achieve the same thing.”
That’s a short definition with a lot of depth.
- “The same thing” means that the people working together are working towards a shared goal in which they have a stake in the outcome (not just the completion).
- “Working together” points towards interdependence, that everyone brings something unique to the work and that shared goal cannot be achieved without each person’s unique contribution.
- “Two or more people” needing each other to achieve a shared outcome requires a shared sense of respect, deep trust, and vulnerability.
It’s easy to forget what “collaboration” means. But we seem to have forgotten how to do it.
What collaboration is not
As people grow more comfortable “collaborating” online, it seems that fewer people are actually collaborating.
Instead, they’re:
- Transacting: There is nothing wrong with email, texts, or messaging someone on your platform of choice. But for the love of goodness, don’t tell me our exchange was a collaboration. If it were, every trip to the ATM would be a team-building exercise.
- Offering choices: When you go out to eat at a fast-food restaurant, do you collaborate with the employee to design your meal? No. You order off a menu. Offering a choice between two or three options (without the opportunity to edit or customize the options), isn’t collaboration. It’s taking an order.
- Complying: Compliance is “the act of obeying a law or rule, especially one that controls a particular industry or type of work.” Following rules isn’t collaboration, it’s following a recipe
- Cooperating: Cooperation is when two or more people work together independently or interdependently to achieve someone else’s goal. Collaboration requires shared objectives and ownership, not just shared tasks and timelines.
There’s nothing wrong with any of these activities. Just don’t confuse them with collaboration because it sends the wrong message to your people.
Why this matters
This isn’t an ivory-tower debate about semantics.
When people believe that simple Q&A, giving limited and unalterable options, following rules, and delivering requests are collaboration, they stop thinking. Curiosity, creativity, and problem-solving give way to efficiency and box-checking. Organizations stop exploring, developing, and innovating and start doing the same thing better, faster, and cheaper.
So, if you truly want your organization to grow because it’s filled with creative and empathetic problem-solvers, invest in reclaiming the true spirit of collaboration. After all, the next big idea isn’t hiding in a chat log—it’s waiting to be born in the spark of genuine collaboration.

by Robyn Bolton | Oct 1, 2024 | Innovation, Leadership, Metrics, Stories & Examples, Strategy
In the often murky world of corporate communication, a leaked MrBeast document has emerged as a beacon of clarity. Far from being your typical vague, jargon-filled memo, this onboarding document is a crystal-clear recipe for success that’s as refreshing as it is rare.
But first, let’s address the elephant in the room. MrBeast’s empire isn’t without its share of controversy. Reports of toxic work environments, unsafe conditions for contestants, and allegations of rigged games cast a shadow over his content creation machine and his leadership capabilities. These are serious issues that merit investigation and discussion. As a result, this post isn’t an endorsement of MrBeast as a leader, it’s an endorsement of an onboarding document that he wrote.
The Secret Sauce: Clarity Meets Innovation
What sets this document apart is its razor-sharp clarity and relentless focus on creativity. Unlike the vague platitudes that plague many corporate communications, job descriptions, and performance matrixes, this document clearly outlines expectations, success metrics, and the strategies and tactics to fuel continuous innovation.
This clarity is transformative for people and organizations. When team members understand both the guardrails and the goals, they channel their creative energy into groundbreaking ideas rather than second-guessing their approach and worrying about repercussions.
Expectations: Always Be Learning
The first principle is a clear directive: always be learning. In MrBeast’s world, this isn’t just about personal growth—it’s about staying ahead in a rapidly changing digital landscape. This commitment to continuous learning fuels innovation by ensuring the team is constantly exploring new technologies, trends, and creative techniques.
While some see the definition of A, B, and C-players as evidence of a toxic workplace, the fact is that it’s the reality in most workplaces. It’s the absence of clarity, usually disguised by claims of family-like cultures that value diversity, that makes workplaces toxic.
Metrics: The Start of a Feedback Loop
The focus on specific success metrics like Click-Through Rate and Average View Duration isn’t just about measurement—it’s about creating a feedback loop for innovation. Clear benchmarks developed over time allow teams to quickly assess the impact of new ideas and iterate accordingly. It also removes the temptation and ability to “move the goalposts” to create the appearance of success.
Strategy: Structure Meets Creativity
After describing what success looks like for employees and how they’ll be measured, the document outlines a structured content formula akin to an innovation strategy. It provides a clear framework of priorities, goals, and boundaries while encouraging creative experimentation within those boundaries.
Starting with a step-by-step guide to making videos with a “wow” factor, the document also emphasizes the criticality of focusing on “critical components” and managing dependencies and
Far from the usual corporate claims that direction and “how to’s” constrain creativity and disempower employees, this approach creates a safety net that allows employees to be successful while still pushing the envelope of what’s possible in content creation.
How to Become Your Version of (a non-controversial) Mr. Beast
You don’t have to be a content creator, social media savant, or company founder to follow MrBeast’s lead. You have to do something much more difficult – communicate clearly and consistently.
- Clearly define what success looks like (and doesn’t) for your employees and projects.
- Establish frameworks that encourage bold ideas while maintaining focus.
- Define objective success metrics and consistently measure, track, and use them.
This leaked MrBeast document offers more than just a glimpse into a YouTube empire; it’s a masterclass in leadership in the era of hybrid workplaces, geographically dispersed teams, and emerging cultures and norms.
The document’s approach shows that innovation doesn’t have to be chaotic. By providing clear expectations and frameworks, leaders can create an environment where creativity thrives, and groundbreaking ideas can be rapidly developed and implemented.
When viewed in the bigger context of the MrBeast organization, however, the document is also a reminder that no matter how clear you think your communication is, you must be vigilant for those who claim that bad behavior is just a “misunderstanding.” Leaders know that no amount of views, clicks, or revenue is worth sacrificing the well-being of their teams.




